
Best adjuvant (assist) for chemotherapy | 1+1>487% |
Effectively improve chemotherapy effect, treatment, immunity.
Reduce side effects and recurrence.
Overview / Relation / Abstract / Role / Principle / Action / Mechanism / Function / Work |
Pleuropulmonary Blastoma - Childhood: Latest Research
Abstract / Summary / Overview of Apoptosis.
Why do cells undergo apoptosis?
The relationship between cancer cells and apoptosis.
Where are the weaknesses and symptoms of cancer cells?
Are cancer cells aggressive?
Extraordinary Solamargine (Role, Principle, Action, Mechanism, Function, Work)
Solamargine's major function mechanism:
Solamargine vs cancer
Best Chemotherapy Adjuvant. (1+1>478%)
Effectively improve chemotherapy effect and cure.
When cancer cells are less resistant to drugs, chemotherapy becomes more effective.
Extract : https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/
Pleuropulmonary Blastoma - Childhood: Latest Research
You will read about the scientific research being done to learn more about this type of tumor and how to treat it.
Doctors are working to learn more about pleuropulmonary blastoma (PPB), ways to prevent it, how to best treat it, and how to provide the best care to people diagnosed with this disease. The following areas of research may include new options for patients through clinical trials. Always talk with your child’s doctor about the best diagnostic and treatment options for your child.
Genetic causes of PPB. As explained in Risk Factors, researchers are continuing to investigate the link between a genetic mutation in DICER1 and PPB in families. Research into causes and treatment for a rare tumor like PPB requires collecting information from many hospitals. The International PPB Registry is the largest such collection of information on PPB in the world. (Please note this link takes you to a separate website.) This registry has approval from the participating institutions’ Institutional Review Boards to ensure the protection of patients’ privacy.
Treatment guidelines. Currently, there are no widely used treatment schedules for PPB because it is so rare. Individual doctors use research and their experience in treating similar conditions, such as soft-tissue sarcomas, to guide their PPB treatment recommendations. Plans are underway to create an international consortium of pediatric oncology specialists from around the world to consider treatment options and make specific recommendations for treating people with PPB.
Screening guidelines. Doctors consider screening for genetic testing for DICER1 in a person who has at least 1 major feature and 2 minor features as listed below:
Major features:
A diagnosis of PPB (any type)
A lung cyst in childhood
Thoracic embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, a type of soft-tissue sarcoma
Cystic nephroma, a benign kidney tumor
Sarcoma in the genitourinary tract, including undifferentiated sarcoma
Ovarian Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor
Gynandroblastoma, a rare ovarian tumor
Uterine, cervical, or ovarian embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma
Neuroendocrine tumor in the genitourinary or gynecologic system
Thyroid nodules or cancer in 2 or more first-degree relatives (such as a parent or child)
Thyroid nodules or differentiated thyroid cancer in childhood
Ciliary body medulloepithelioma, a type of childhood eye tumor
Nasal chondromesenchymal hamartoma, a benign tumor in the nasal sinus area
Pineoblastoma, a cancerous tumor of the brain’s pineal gland
Pituitary blastoma, an aggressive tumor of the pituitary gland
Minor features:A lung cyst in an adult
Renal (kidney) cysts
Wilms tumor, a childhood kidney cancer
Thyroid nodules or differentiated thyroid cancer in an adult
Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma not listed under "Major features" (see above)
Neuroendocrine tumor that is poorly differentiated
Undifferentiated sarcoma somewhere besides the genitourinary tract
Macrocephaly, an overly large head size in childhood
Childhood cancers associated with any Minor features
Source: Clinical Cancer Research 2018 May 15;24(10):2251-2261. doi: 10 (Table 1).If a person is found to have DICER1, doctors will consider screening them further for specific conditions based on specific signs and symptoms that are reported to the doctor or found on a physical exam to look for problems (including those listed above in Major and Minor Features) in these main body systems:
Lung system – Symptoms include abnormally rapid breathing, cough, fever, pain, and a collapsed lung. Screening tests include regular chest x-rays or a chest CT scan.
Thyroid gland – Symptoms include a nodule or growth on the thyroid gland that is visible or can be easily felt, persistent enlargement of neck lymph nodes, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, neck pain, and cough. Screening tests include regular thyroid ultrasounds and regular physical exams to check the thyroid.
Gynecologic system – Symptoms include dark, coarse, male-pattern hair growth in females, development of other male characteristics such as a deepening voice in females, and abdominal pain, expansion, or a mass. Screening tests include regular pelvic and abdominal ultrasounds.
Kidneys/genitourinary system – Symptoms include an abdominal mass or pain, or blood in the urine. Screening tests include regular abdominal ultrasounds.
Gastrointestinal system – Symptoms include any sign of intestinal obstruction, such as cramps, constipation, vomiting, or abdominal swelling. Doctors will talk with a person about what screening tests may be appropriate for them.
Central nervous system (CNS) and the head and neck system – This includes symptoms that do not involve the thyroid gland (see above), such as headaches, vomiting, double-vision, inability to look upward, difficulty walking, premature puberty, Cushing’s syndrome, vision problems, and nasal obstruction. Screening tests include regular physical exams, annual ophthalmologic exam including visual acuity screening, as well as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for emergency symptoms inside the skull.
Source: Clinical Cancer Research 2018 May 15;24(10):2251-2261. doi: 10 (Table 2).
Doctors are looking at ways to screen children for PPB and other cancers related to DICER1 genetic mutations. For PPB, screening guidelines will help doctors know when it’s best to use a computed tomography (CT) scan to look for possible lung cysts or tumors, particularly for children under the age of 3. MRIs of the brain for children with the DICER1 germline mutation are also being evaluated for screening guidelines.
Abstract / Summary / Overview of Apoptosis.
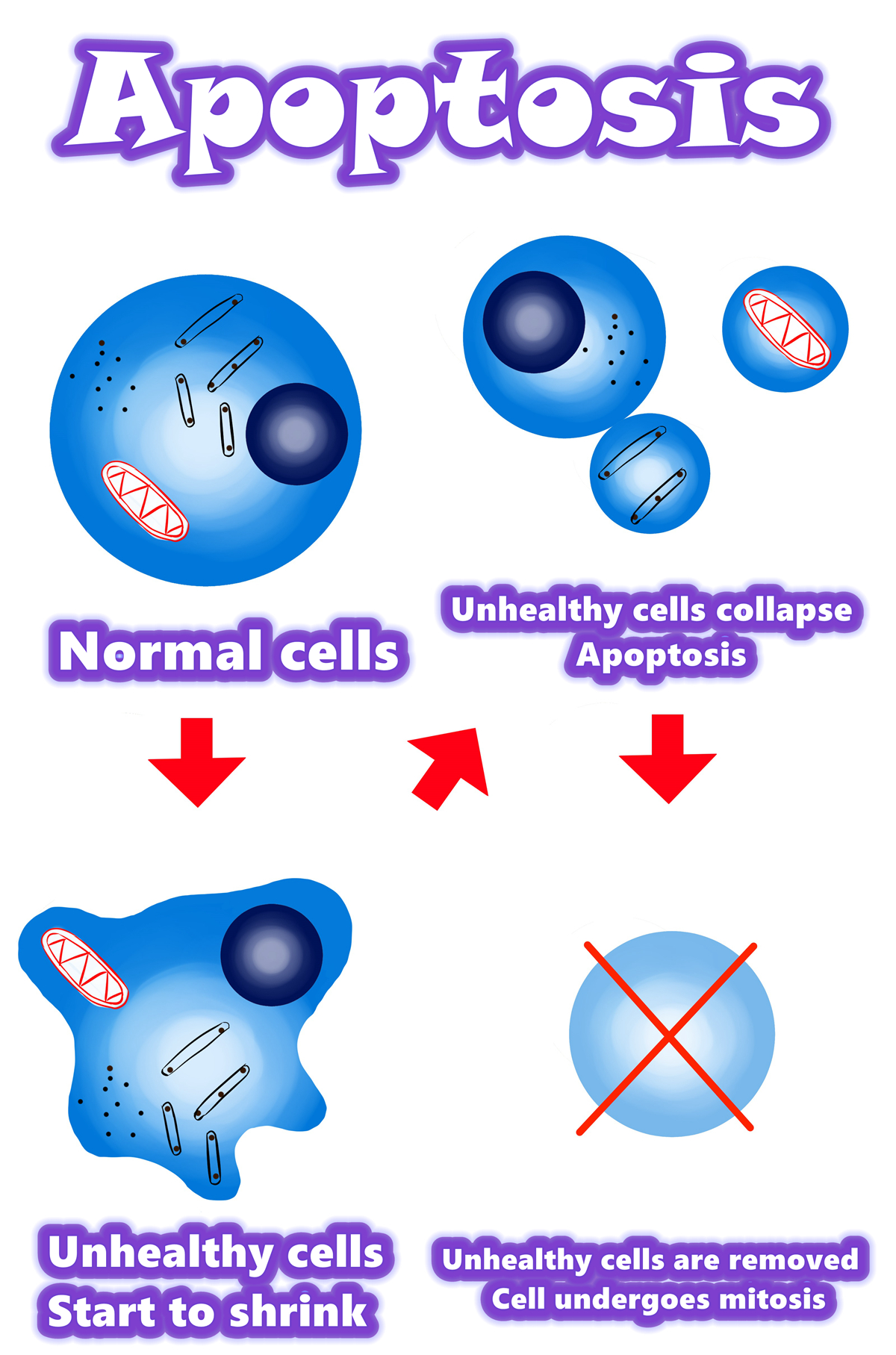
Overview of apoptosis
•Programmed cell death
•Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death, or “cellular suicide.”
•Apoptosis is different from necrosis, in which cells die due to injury.
•Apoptosis removes cells during development, eliminates potentially cancerous and virus-infected cells, and maintains balance in the body.
Why do cells undergo apoptosis?
- Basically, apoptosis is a general and convenient way to remove cells that should no longer be part of the organism.
- Some cells are abnormal and could hurt the rest of the organism if they survive, such as cells with viral infections or DNA damage.
- Apoptosis is part of development
- In many organisms, programmed cell death is a normal part of development.
The relationship between cancer cells and apoptosis
Apoptosis can eliminate infected or cancerous cells.
When a cell’s DNA is damaged, it will typically detect the damage and try to repair it.
If the damage is beyond repair, the cell will normally send itself into apoptosis, ensuring that it will not pass on its damaged DNA.
When cells have DNA damage but fail to undergo apoptosis, they may be on the road to cancer.
However, “successful” cancer cells successfully evade the process of apoptosis.
This allows them to divide out of control and accumulate mutations (changes in their DNA).
Apoptosis is key to immune function
Apoptosis also plays an essential role in the development and maintenance of a healthy immune system.
Where are the weaknesses and symptoms of cancer cells?
The symptoms of cancer cells are in the nucleus.
The nucleus controls the outer cytoplasm, cell composition, cell viability, etc.
DNA mutations also mutate in the nucleus.
Therefore, to treat cancer cells, we must first enter the nucleus.
Let the “regulatory cell gene” mechanism enter the nucleus to regulate
Are cancer cells aggressive?
After the action of Solamargine, the aggressiveness of cancer cells is alleviated.
So after using Solamargine, many patients feel that I am half better.
Although the tumor does not disappear quickly, patients feel that the degree of aggressiveness is reduced.
Extraordinary Solamargine (Role, Principle, Action, Mechanism, Function, Work).
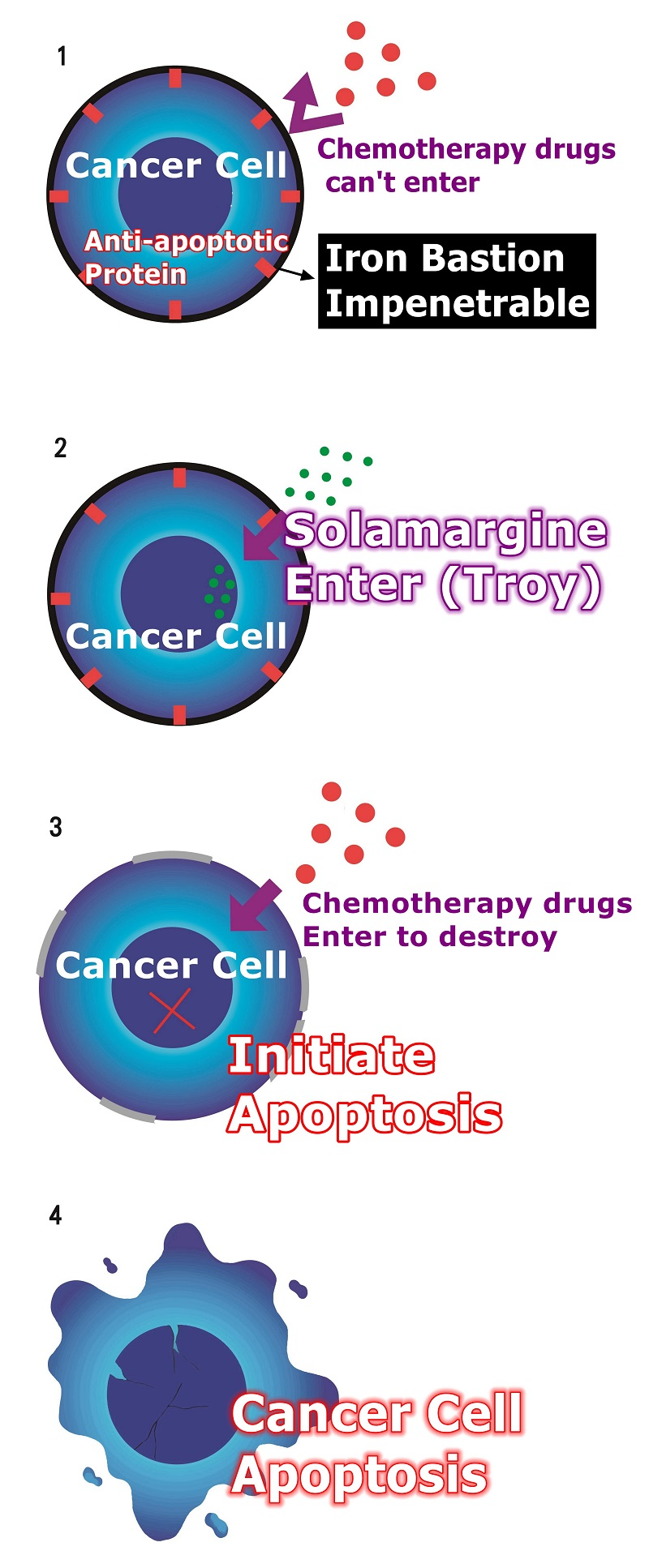
Solamargine's major function mechanism:
When Solamargine enter,
Solamargine activates receptors that are turned off by cancer cells, allowing cancer cells to modulate again.
Solamargine modulates the anti-modulates genes of cancer cells, making cancer cells less resistant.
Reduced drug resistance
When cancer cells are less resistant to drugs, chemotherapy becomes more effective.
Solamargine modulates the mutated genes in cancer cells and then initiates cancer cell apoptosis to achieve anti-cancer effects.
Solamargine combined with which chemotherapy drugs are more effective in treating cancer cells?
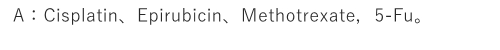
Solamargine vs cancer
Solamargine vs cancer
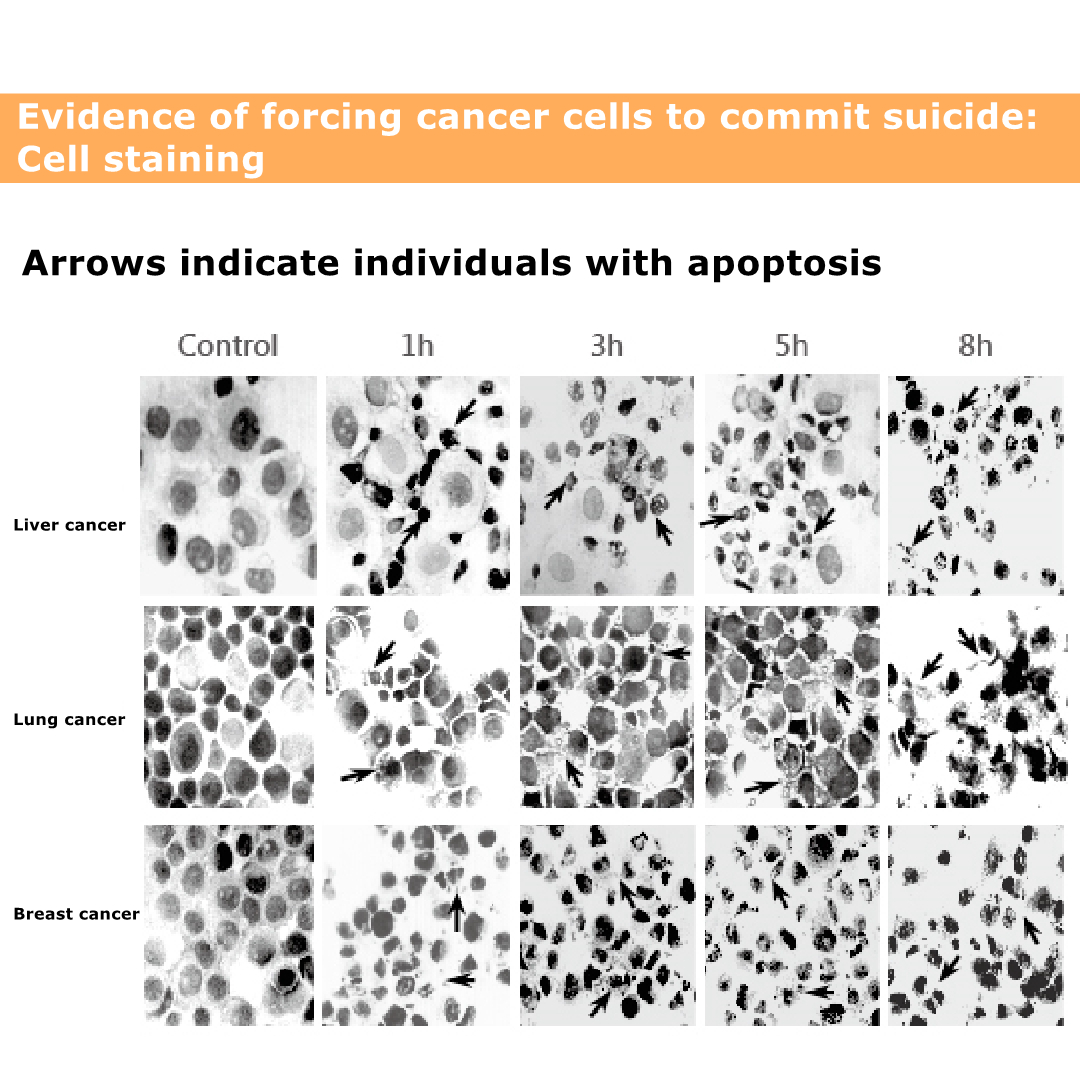
The picture shows the death of cancer cells.
The black and black parts are cancer cell nuclei.
Even if the nucleus ruptures, the cancer cells will die.
The figure shows that cancer cells can cause death.
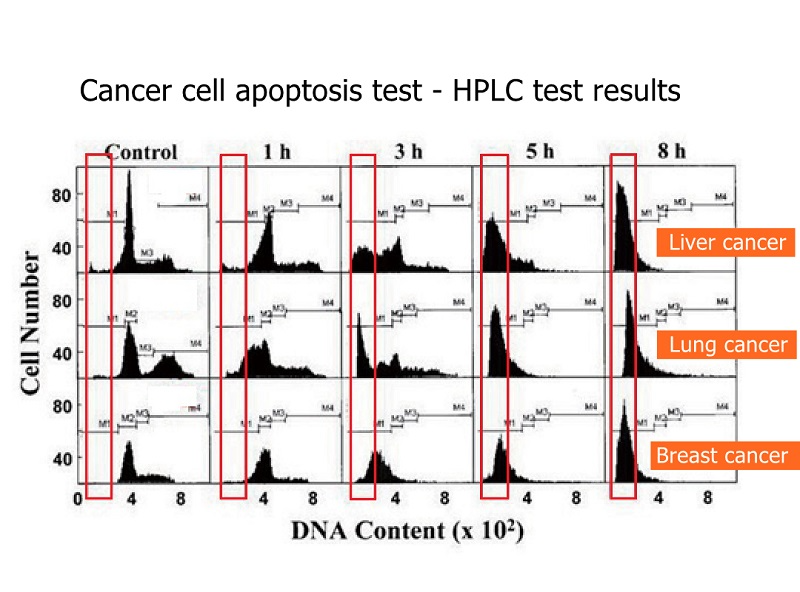
The figure shows that cancer cells can cause death.
The figure shows that the death of lung cancer cells is relatively slow, and it will not be obvious until eight hours later.
The figure shows that the death of liver cancer cells is very obvious, even more obvious in eight hours.
The graph shows that breast cancer cells die faster. It was obvious from the beginning that breast cancer is easy to treat, and patients with breast cancer need not worry.
Best Chemotherapy Adjuvant. (1+1>487%)
Effectively improve chemotherapy effect and treatment.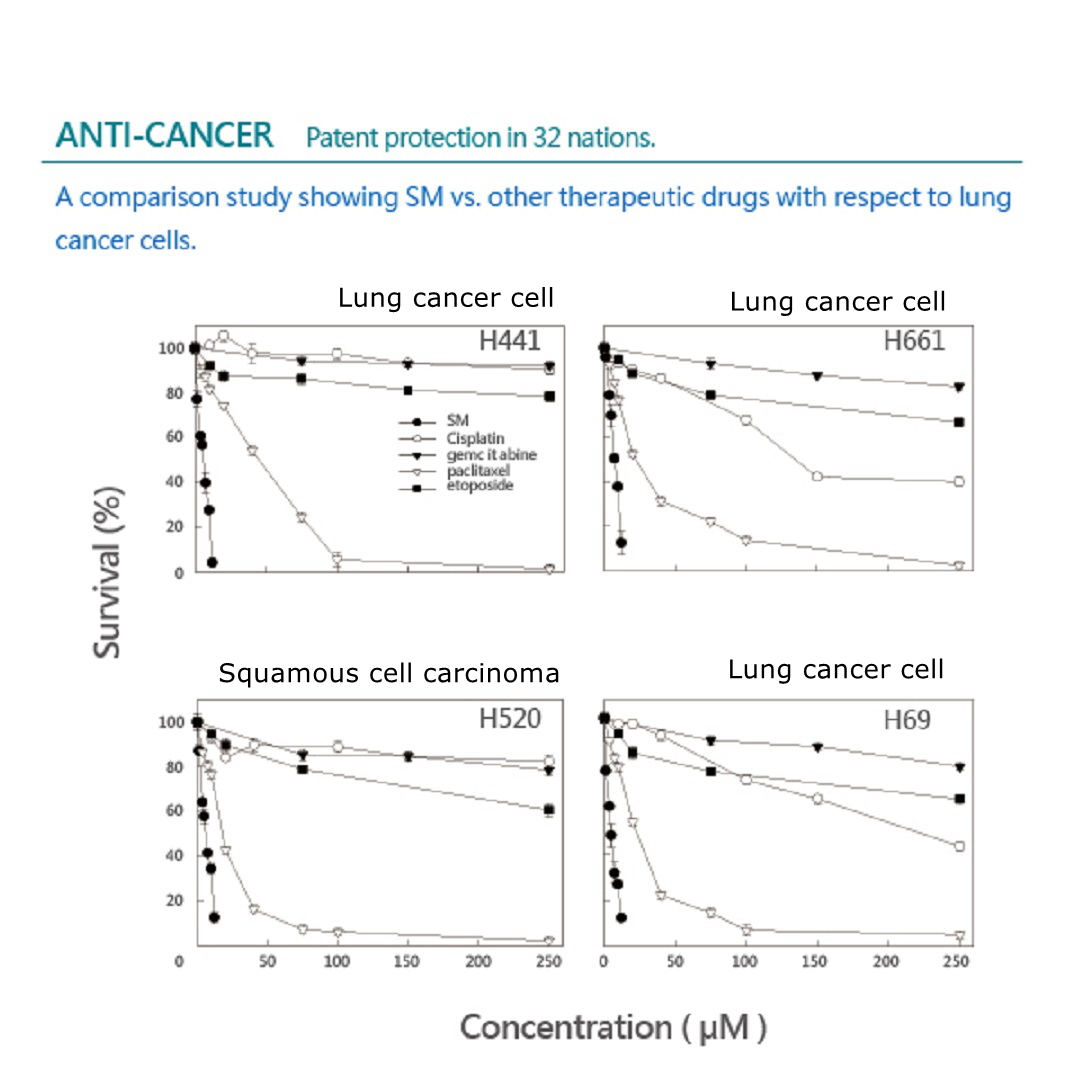
ANTI-CANCER
Patent protection in 32 nations.
A comparison study showing Solamargine vs. other therapeutic drugs with respect to lung cancer cells.
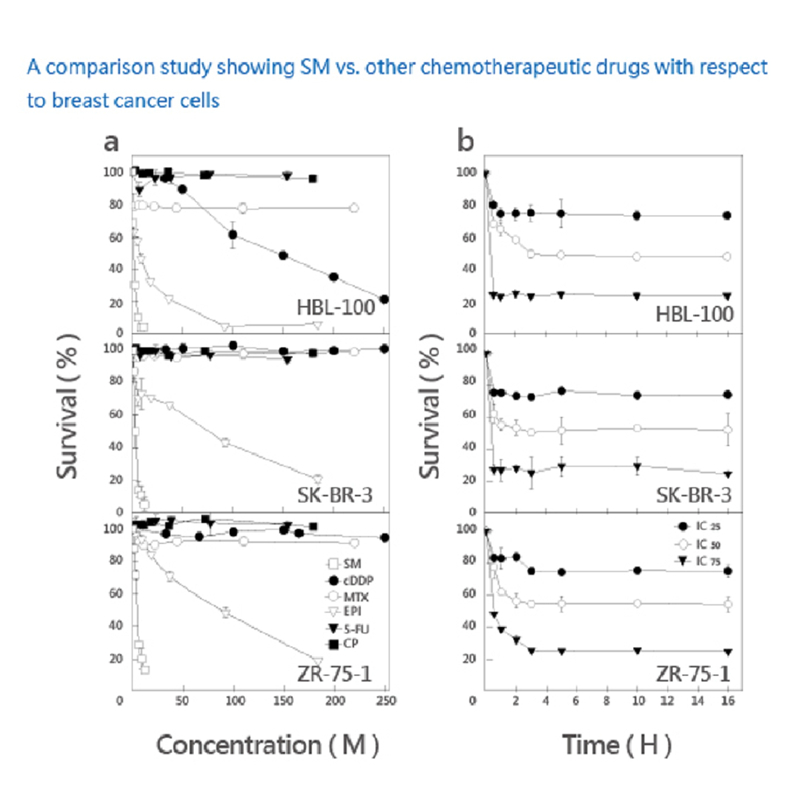 A comparison study showing Solamargine vs. other chemotherapeutic drugs with respect to breast cancer cells.
A comparison study showing Solamargine vs. other chemotherapeutic drugs with respect to breast cancer cells.
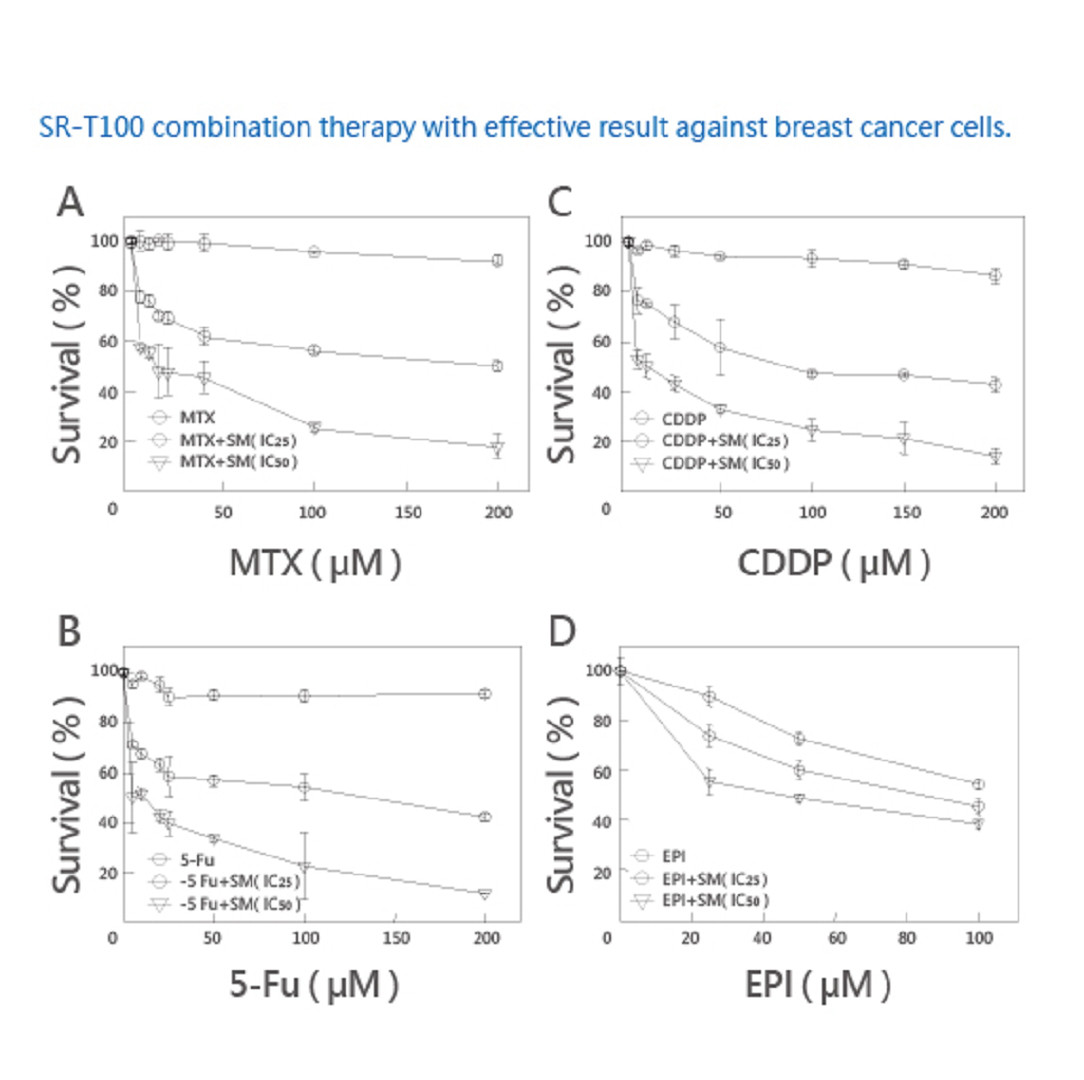
SR-T100 combination therapy with effective result against breast cancer cells.
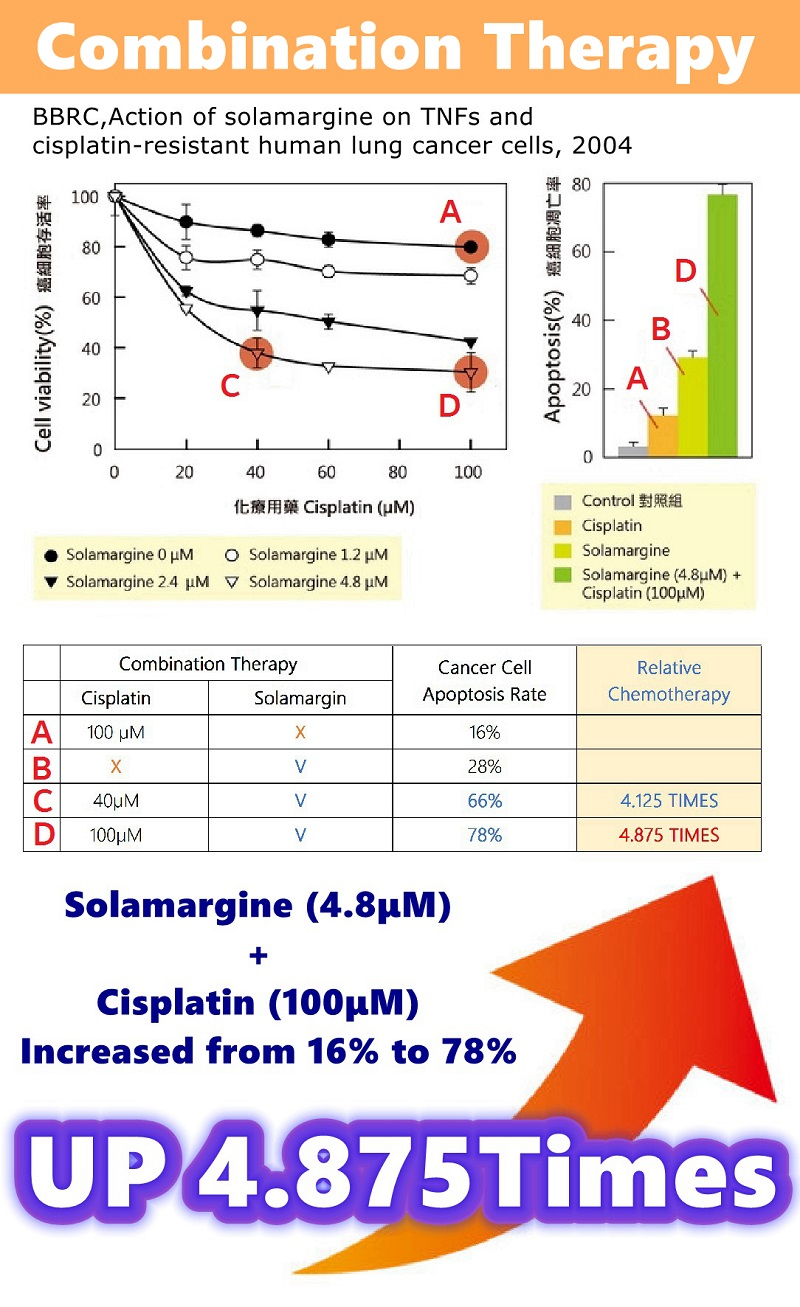
Combination Therapy | Research results for lung cancer cells.
A. Chemotherapy (100μM), 16% of cancer cell apoptosis.
B. Alone SM (4.8μM), 28% of cancer cell apoptosis.
C. SM (4.80μM) + Chemotherapy (40μM), 66% of cancer cells apoptosis.
D. SM (4.80μM) + Chemotherapy (100μM), 78% of cancer cell apoptosis.
SM has a clearing effect better than Chemotherapy.
The combined treatment of Solamargine and Chemotherapy significantly increased the apoptosis of lung cancer cells.
SM (4.8μM) + Chemotherapy (40μM), increased from 16% to 66% (up to 4.125 times).
SM (4.8μM) + Chemotherapy (100μM), increased from 16% to 78% (up to 4.875 times).
Reorganized from: BBRC. Action of Solamargine on TNFs and drug-resistant human lung cancer cells 2004.
The best solution for cancer cells.
